Ad Block Detected!
Our website is made possible by displaying ads to our visitors. Please support us by whitelisting our website or allowing necessary trackers.
Our website is made possible by displaying ads to our visitors. Please support us by whitelisting our website or allowing necessary trackers.
A way of visiting different nodes on a graph. There are two types, Depth first (using a stack) and breadth first (using a queue)
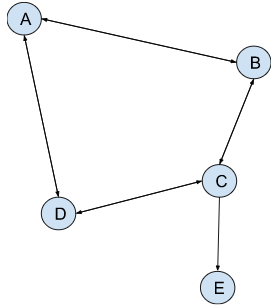
First, push A onto the stack and mark it as visited. Then Push B onto the stack and mark it as visited (you choose from either B or D).
Next, you push C to the stack and mark it as visited
You then push E to the stack (you can choose E or D).
Because node E has no neighbors, we remove it from the stack and see if node C has any neighbors that haven't already been visited. Node D has not been visited, so it is pushed to the top of the stack.
D has no neighbors, so it is popped. C has no unvisited neighboring nodes, so it is popped, as are B and A. The stack is now empty, and the search is finished.

First, we enqueue (add) the a node onto the queue which is A.
Next, we visit all of its neighboring nodes and enqueue them onto the queue.
Since there are no more neighboring nodes, A is dequeued (removed) from the queue. It's now been visited. Remember it’s first in first out (FIFO) with queues.
Now you enqueue all the connecting nodes of B.
B has been dequeued because it no longer has any connected nodes. D is also dequeued because there are no connecting nodes.
Finally, we enqueue all of node C's neighbors. E is enqueued.
Since E has no neighboring nodes, C is dequeued along with E since it too has no neighbors that haven't already been visited.